While often operating behind the scenes, the maintenance industry plays a crucial role in supporting the global workforce. It ensures economic stability, guarantees safety, and promotes operational efficiency [...]

While often operating behind the scenes, the maintenance industry plays a crucial role in supporting the global workforce. It ensures economic stability, guarantees safety, and promotes operational efficiency across various sectors—from manufacturing to logistics and beyond. As the industry continues to expand, new technologies and innovative approaches are shaping maintenance processes, making them more efficient, accurate, and sustainable.
In this article, we present 10 fascinating maintenance metrics and statistics for 2024 that highlight the evolving state of the industry. Understanding these key insights will help you stay informed and better prepare for the future of maintenance.
Maintenance market overview
As businesses across various sectors continue to recognize the importance of regular maintenance, the industry has experienced significant growth in recent years. In this section, we will explore key metrics that illustrate the current state and future potential of the maintenance market, beginning with the market’s overall value and growth projections.
Metric 1: Market value of the maintenance industry
According to a study published by Fortune Business Insight, the global inspection, repair, and maintenance market is experiencing substantial growth. Valued at $40.25 billion in 2021, the market grew to $42.66 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach $72.46 billion by 2029, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.9%. This rapid expansion highlights the increasing demand for maintenance solutions worldwide, driven by advancements in technology and a focus on improving operational efficiency. In 2021, the Asia Pacific region led the global market, accounting for 26.73% of the market share, reflecting the region’s growing industrial and economic activity.
Maintenance workforce insights
The maintenance industry is not only growing in terms of market value but also offers numerous employment opportunities across a wide range of roles. In this section, we take a closer look at the current state of the maintenance workforce, including job numbers, employment growth, and demographics.
Metric 2: Workforce size and employment growth
Just in the US alone, the maintenance and repair industry employs more than 1.6 million individuals, with this number expected to rise. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the sector was projected to add 57,200 jobs by 2032, representing a 4% growth rate. This steady growth reflects the increasing need for skilled maintenance professionals to support various industries. Maintenance roles are diverse, spanning a wide range of responsibilities and skill sets. Common positions include HVAC technicians, electricians, plumbers, aircraft and automotive technicians, groundskeepers, and custodians.
Metric 3: Age demographics of maintenance professionals
The maintenance workforce is characterized by a significant proportion of experienced professionals. A 2023 survey conducted by Plant Engineering revealed that 69% of maintenance workers are aged 50 or older, with an average age of 54 years. The survey, which polled 243 workers in the general maintenance and repair industry, also found that these professionals work an average of 46 hours per week, have 26 years of experience in the manufacturing sector, and have been with their current employer for an average of 14 years.
These statistics indicate that the industry is heavily reliant on a seasoned workforce, which presents both opportunities and challenges for the future. As older workers near retirement, there will be an increasing need for younger professionals to fill the gap and ensure the continued efficiency and reliability of maintenance operations. For more insights into the current skills shortage in the German industry, be sure to check out this article.
Effectiveness of maintenance programs
Investing in effective maintenance programs can significantly enhance an organization’s productivity and reduce costly downtime. By examining key metrics, we can better understand the positive impact that well-executed maintenance strategies have on operations. Below, we explore how comprehensive maintenance programs reduce downtime and how digitization can improve efficiency by minimizing the time spent on physical work orders.
Metric 4: Reduction in downtime due to maintenance programs
Investing in comprehensive maintenance and repair programs has a significant impact on reducing downtime within organizations. On average, downtime is decreased by 44%, resulting in more efficient operations and less disruption. A 2021 report by the International Journal of Prognostics and Health Management also highlighted additional benefits: organizations experienced a 54% reduction in defect rates, 35% fewer lost sales due to defects, and 29% fewer lost sales due to maintenance-related delays. These improvements showcase the critical role that proactive maintenance strategies play in maintaining productivity and quality.
Metric 5: Time spent on physical work orders
A key challenge faced by maintenance professionals is the time spent managing physical work orders and documentation—approximately 45% of their working hours according to a study published in Big Data in Manufacturing, Biology, Healthcare and Life Sciences. This inefficiency can be greatly reduced through the adoption of a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS), which centralizes all maintenance activities on a single digital platform. By digitizing work orders and allowing remote access, CMMS software streamlines processes, enhances accessibility, and reduces the time spent retrieving documents. As a result, organizations benefit from reduced downtime, lower labor costs, and increased overall operational efficiency and profitability.
Impact of maintenance on operations
The maintenance of equipment and machinery plays a critical role in ensuring smooth operations within an organization. Neglecting this aspect can lead to significant revenue losses and operational challenges. Below, we explore key metrics related to the impact of maintenance on downtime and how aging equipment affects overall efficiency.
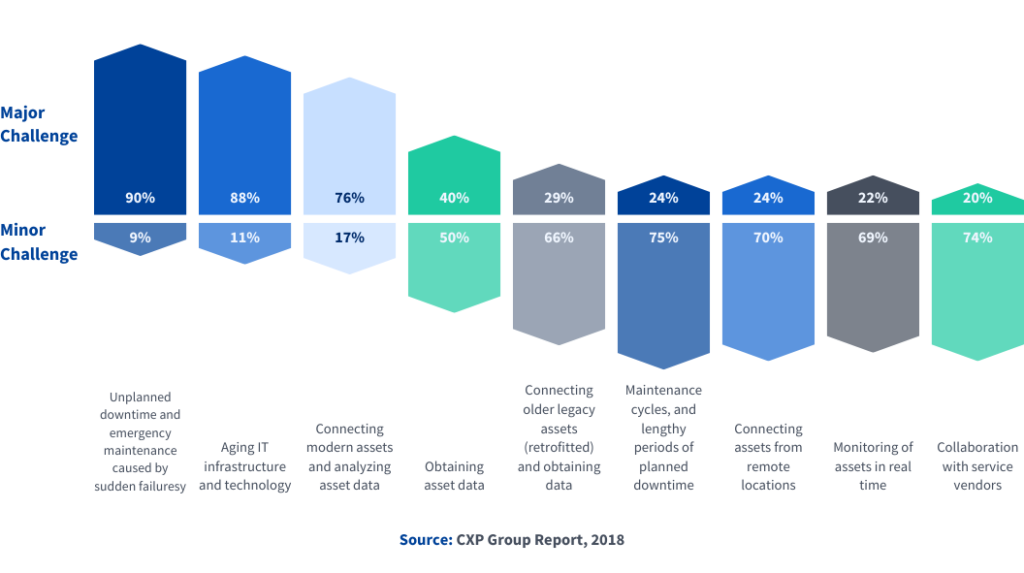
Metric 6: Downtime and revenue loss
Unplanned downtime can be one of the most expensive challenges for large organizations, with Fortune Global 500 companies experiencing an annual total of $1.4 trillion in losses due to such disruptions. To put it into perspective, that’s $1.4 trillion—roughly equivalent to the annual GDP of a major industrial nation like Spain. According to this 2024 Siemens report, these losses represent 11% of their cumulative annual revenues—though it’s worth noting that this figure has decreased by 6% since 2022, showcasing some progress in reducing downtime through improved maintenance practices.
Further emphasizing the severity of the problem, recent research highlighted by Forbes reveals that the average cost of downtime for large organizations can reach as high as $9,000 per minute. For higher-risk industries, such as healthcare, the cost can soar beyond $5 million per hour, excluding any fines or penalties that may arise. This staggering cost underscores the importance of proactive maintenance strategies to minimize downtime and protect revenue streams.
Metric 7: Aging equipment and operational inefficiencies
Aging equipment is a significant contributor to operational inefficiencies, with 80% of manufacturing plants citing machinery breakdowns as their leading cause. The 2022 Plant Engineering survey also identified other key factors impacting efficiency, such as difficulties in recruiting skilled labor (49%) and the challenges of integrating digital management technologies with legacy equipment (41%).
These findings underscore the need for organizations to prioritize both equipment upgrades and workforce development, while also adopting digital solutions that can bridge the gap between modern maintenance practices and aging machinery.
Maintenance strategies statistics
The effectiveness of maintenance strategies can significantly impact operational efficiency and profitability. Organizations are increasingly recognizing the need to evaluate and optimize their maintenance approaches. This section delves into two crucial metrics that reveal the stark differences between reactive and preventative maintenance strategies, as well as the main challenges that companies face in the evolving maintenance landscape.
Metric 8: Reactive vs. preventative maintenance
Organizations that relied predominantly on reactive maintenance, rather than employing a mix of alternative maintenance strategies, experienced significantly more operational disruptions—3.3 times more downtime, to be exact. Beyond this, the repercussions of a reactive approach were substantial: 16 times more defects, 2.8 times more lost sales due to those defects, 2.4 times more lost sales due to maintenance-related delays, and an increase in inventory by nearly fivefold (4.89 times) due to various maintenance issues. These metrics underscore the importance of shifting towards a more proactive, preventative maintenance strategy to minimize disruptions and costs.
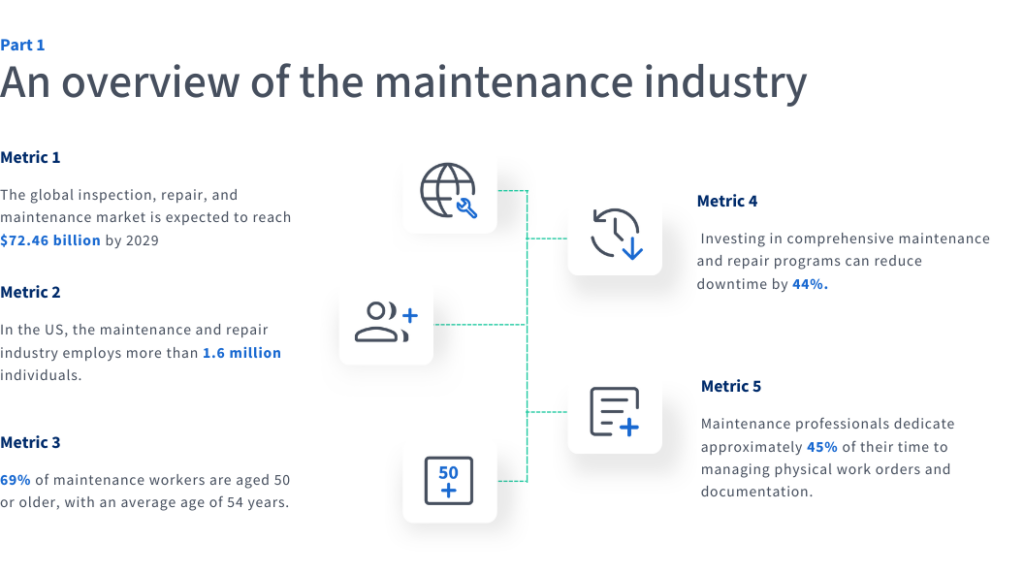
Metric 9: Main pain points
In the evolving landscape of maintenance, many organizations are grappling with persistent challenges. For European companies, the primary issues include unplanned downtime and emergency maintenance, which affect 90% of businesses according to the CXP Group Report. Aging IT infrastructure and outdated technology also present difficulties for 88% of companies, while 76% struggle with connecting modern assets and analyzing the resulting data. Other notable pain points include challenges in obtaining asset data (40%), connecting legacy assets (29%), managing maintenance cycles (24%), linking assets from remote locations (24%), monitoring assets in real time (22%), and collaborating effectively with vendors (20%). These pain points highlight the need for modern maintenance strategies and technological upgrades to support better efficiency and resilience.
Maintenance technologies
The implementation of advanced maintenance technologies is essential for organizations striving to enhance their operational efficiency. Among these technologies, Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) have emerged as a key solution, with a significant percentage of facilities adopting them to optimize their maintenance and repair operations. This shift towards digital management is indicative of a broader trend where organizations seek to integrate various maintenance management software solutions to meet their evolving needs.
Metric 10: Adoption of CMMS software
The adoption of Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) software has become a pivotal trend in modern maintenance practices, with 59% of facilities utilizing these systems to manage their maintenance and repair operations. A 2022 survey by Plant Engineering highlights that many organizations are integrating multiple maintenance management software solutions within their facilities. Among the respondents, 39% reported using an enterprise asset management system, while 19% opted for plant floor or manufacturing execution software. When it comes to installation and deployment, 48% of respondents indicated they use on-premise systems, 30% prefer cloud-based solutions, and 22% have adopted hybrid approaches. Additionally, 18% reported using software as a service (SaaS), and 14% utilized mobile systems. This diverse adoption of CMMS technologies showcases a growing commitment to enhancing operational efficiency and streamlining maintenance processes, allowing organizations to adapt effectively to the ever-evolving technological landscape.
Elara’s perspective
We at Elara observe that the maintenance industry is undergoing significant transformation as organizations increasingly embrace advanced technologies and proactive strategies to optimize their operations. By leveraging the fascinating statistics presented in this article, businesses can better understand the importance of evolving their maintenance practices to enhance efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve overall performance.
To see how our customers have successfully implemented these changes and harnessed the power of innovative maintenance strategies, explore our success stories.
[In the age of AI, you never know if you’re reading something copy and pasted directly from ChatGPT, or if an actual human sat down to write this with some cool facts from their boss or operations team. That’s why we created a short and simple introduction to how we create content at Elara.]