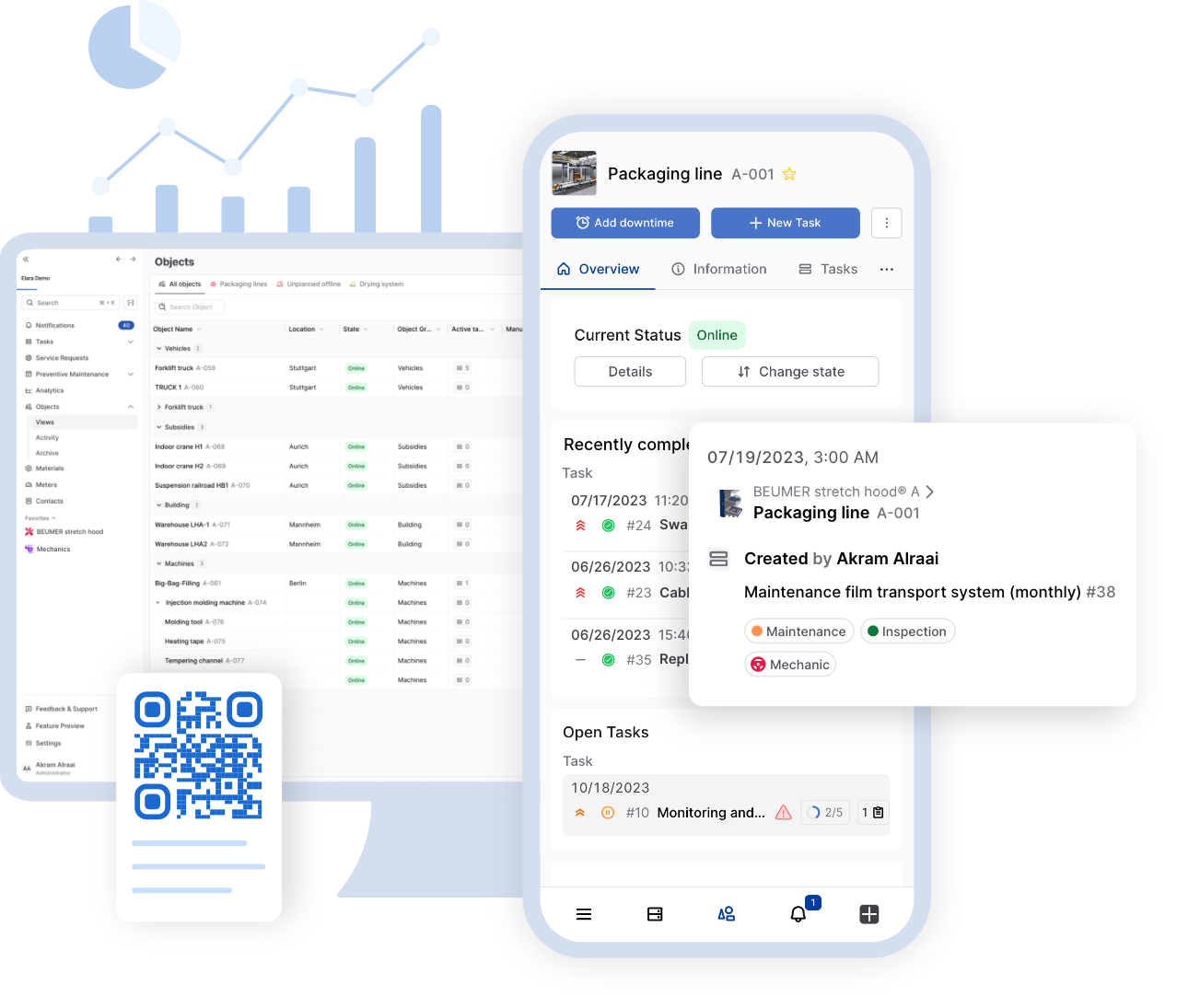
A work order is a document issued for maintenance, repair, or operational tasks, containing all necessary information such as work details, required resources, and instructions for execution. It [...]

A work order is a document issued for maintenance, repair, or operational tasks, containing all necessary information such as work details, required resources, and instructions for execution. It serves as a central tool for managing, assigning, and tracking maintenance activities, ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and in line with operational objectives.
Work orders ensure that maintenance tasks are carried out properly and efficiently and provide a foundation for planning future maintenance actions. In this article, we define what a work order is and offer tips on how to effectively structure digital work orders to optimize the maintenance process.
Definition of a work order
A work order is a documented instruction outlining the maintenance tasks to be performed on a piece of equipment or machinery. It includes all necessary details, such as the specific equipment to be serviced, the type of maintenance required, the urgency of the task, the responsible team member, and the current status of the work.

Key categories for digital work orders
To better organize and streamline work orders, it is useful to categorize them. Here are some of the most important categories to consider when creating work orders:
1. Equipment or machinery
The specific equipment or machinery affected should be clearly indicated in the work order. This facilitates the maintenance team’s identification of the digital work instruction and the procurement of necessary resources and materials. Categorizing by machinery also allows for later analysis of the maintenance history.
2. Type of maintenance
The type of maintenance is a crucial category that helps in planning the workload and required resources. Various types of maintenance can be distinguished, including:
- Preventive maintenance: Regular, scheduled maintenance tasks to prevent breakdowns.
- Corrective maintenance: Repair tasks performed to fix an existing problem.
- Predictive maintenance: Maintenance measures designed to prevent potential issues before they occur.
- Condition-based maintenance: Maintenance tasks performed based on specific conditions, such as operating hours.
- Breakdown maintenance: Actions taken to repair or replace damaged parts after a breakdown.
- Safety and environmental maintenance: Maintenance tasks ensuring operational safety and environmental compliance.
- Planned maintenance: Maintenance carried out during a scheduled shutdown.
- Emergency maintenance: Unexpected maintenance tasks that need to be completed urgently to bring equipment back online quickly.
3. Urgency
Prioritizing work orders by their urgency is essential to ensure that the most critical tasks are completed first. This can be done using a numerical scale, for example.
4. Responsible person
Assigning a responsible person to each work order ensures clarity on who is in charge of completing the tasks and serves as a point of contact for any questions.
5. Work order status
The status of the work order, such as “in progress,” “waiting for materials,” or “completed,” helps the maintenance team stay organized and avoid delays.

Practical implementation with maintenance software
Structuring work orders can be done in various ways. While simple Excel spreadsheets are one option, using maintenance software like Elara’s is far more efficient. This software comes with pre-configured categories and allows for easy and quick digital creation of work orders.
Benefits of Elara’s maintenance software:
- Automatic assignment: Complex assignments to machinery and spare parts are automatically implemented.
- Customizable maintenance types: Maintenance types can be individually customized and directly applied, such as for calculating OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness).
- Real-time tracking: The software enables real-time tracking of work progress.
- Optimization analytics: Analysis tools help optimize maintenance processes by identifying and addressing bottlenecks early on.
Elara’s perspective
Based on our expertise in the maintenance industry, we know that a well-structured approach to digital work orders is crucial for ensuring efficiency and organization in maintenance processes. A well-thought-out work order forms the backbone of a successful maintenance strategy. However, the challenges companies face can be varied, from the complexity of machinery and equipment to the need to minimize downtime and comply with stringent safety and environmental standards.
This is where Elara Maintenance Software comes into play. Our solution is specifically designed to tackle these challenges and optimize the entire work order management process. With Elara, companies can not only create and assign work orders more efficiently but also conduct in-depth analyses of their maintenance activities. This leads to better resource planning, shorter response times to disruptions, and ultimately, higher equipment availability.
For companies that have not yet implemented maintenance software, introducing Elara can make a significant difference. By automating many administrative tasks and providing real-time data, Elara streamlines maintenance processes and allows your team to focus on the essential tasks. The software is flexible and adapts to the specific needs of your company, giving you full control over your maintenance activities while simultaneously increasing efficiency.
Want to hear what our customers have to say about Elara? Then check out our success stories.
[In the age of AI, you never know if you’re reading something copy and pasted directly from ChatGPT, or if an actual human sat down to write this with some cool facts from their boss or operations team. That’s why we created a short and simple introduction to how we create content at Elara.]