Maintenance activities encompass all activities aimed at preserving or restoring the functionality of machinery, equipment, buildings, and other assets. These tasks are carried out either according to a [...]

Maintenance activities encompass all activities aimed at preserving or restoring the functionality of machinery, equipment, buildings, and other assets. These tasks are carried out either according to a predetermined schedule or as needed.
Effective maintenance is a critical and complex responsibility, playing a vital role in operational success. However, many companies struggle with this, as manual processes and reliance on paper documentation complicate the task. The resulting challenges, such as time-consuming administration, increased error risk, and limited transparency, often lead to inefficiencies, excessive costs, and preventable downtime.
In this article, we offer a detailed overview of various maintenance strategies and their advantages. Additionally, we share best practices that can help maintenance managers implement these strategies more efficiently.
Benefits of maintenance activities
Maintenance activities offer a range of significant advantages that not only enhance the efficiency of operations but also contribute to cost reduction.
Key benefits include:
- Increased uptime: Regular maintenance and servicing reduce the likelihood of breakdowns, ensuring maximum operational availability of equipment and machinery.
- Cost savings: Proactive, scheduled maintenance helps prevent costly repairs and unexpected downtime, leading to a substantial decrease in overall expenses.
- Enhanced safety: Routine inspections and upkeep of machinery and equipment minimize the risk of accidents and hazards, creating a safer working environment for employees.
- Extended asset lifespan: Well-targeted maintenance activities prolong the life of machines and systems, reducing the need for frequent replacements and saving on capital investment.
What types of maintenance activities are there?
According to DIN 31051 (fundamentals of maintenance), maintenance activities are categorized into four main types. A comprehensive maintenance strategy should typically encompass all of these categories. However, depending on the company, customer needs, or the specific equipment in use, it may be practical to exclude certain measures or delegate them to external service providers.
1. Inspections
Inspections are a fundamental type of maintenance, involving the routine assessment of machines and systems to monitor their current condition. These preventive actions help detect potential issues early, allowing for timely corrections before major malfunctions occur. Inspections involve checking various parameters such as wear, fluid levels, and overall safety aspects. Documenting inspection results not only ensures a clear understanding of equipment conditions but also supports compliance with legal and safety standards. A well-organized inspection process enhances transparency and improves the scheduling of maintenance and repair activities.
2. Maintenance
Maintenance encompasses all activities aimed at preserving the functionality of machines and systems or ensuring they remain in optimal condition. This includes routine tasks such as lubricating moving parts, replacing filters, and replenishing fluids. Properly targeted maintenance minimizes the risk of unexpected failures and extends the lifespan of equipment. Maintenance intervals should be scheduled based on both manufacturer recommendations and operational conditions to maintain peak performance. When executed effectively, maintenance not only boosts operational efficiency but also helps lower the overall cost of ownership.
3. Repair
Repair involves the actions required to restore defective or damaged machinery and systems to full working order. In essence, it focuses on returning the equipment to its original, functional state. This type of maintenance typically occurs after a breakdown or malfunction and often includes the repair or replacement of faulty components. Prompt repairs are essential to quickly resume production processes and minimize financial losses. Proper documentation of repairs is crucial for identifying recurring issues and preventing future failures. Successful repair strategies depend on technical expertise and efficient use of materials to keep costs manageable.
4. Improvement
Improvement measures focus on enhancing the performance and efficiency of machines and systems beyond their original state, without altering their fundamental functions. These upgrades can be achieved through technical modifications, modernization efforts, or the integration of new technologies. Improvements boost productivity, reduce energy consumption, and optimize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). By continuously analyzing operational data, companies can refine their maintenance strategies and drive ongoing optimization. Investing in improvement measures not only strengthens competitiveness but also fosters a culture of continuous development and innovation.

Best practices for effective maintenance implementation
The complexity and daily demands of maintenance are often underestimated. To optimize resource use and ensure efficient operations, thorough organization and planning are essential, along with the right choice of tools. To help streamline maintenance processes, we recommend the following best practices:
1. Select the right maintenance strategy
Defining clear objectives is key to shaping a maintenance strategy, whether the goal is to maximize asset uptime or minimize operational costs. Start by thoroughly analyzing your existing equipment and systems to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. Based on this assessment, select the most suitable approach—such as preventive or predictive maintenance—to enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of your maintenance efforts. For a deeper dive into different maintenance strategies, explore our detailed blog article.
2. Conduct regular training
Regularly train your maintenance staff to keep them updated on the latest technologies and methodologies. Ongoing training not only enhances their technical skills but also boosts motivation and fosters a stronger awareness of safety protocols.
3. Leverage maintenance software
Implement modern maintenance software to streamline the planning, execution, and documentation of maintenance tasks. This increases operational efficiency, improves transparency, and provides real-time insights into maintenance activities.
4. Develop a maintenance plan
A well-structured maintenance plan is fundamental to any effective strategy, ensuring the smooth operation of machinery and systems. Establish maintenance intervals based on manufacturer guidelines and practical experience, outlining specific tasks to be completed. Prioritize critical tasks while considering available resources, time, and budget. A comprehensive maintenance plan maximizes equipment availability, optimizes costs, and significantly improves overall maintenance efficiency. You can download our free maintenance plan template here to get started.
4. Foster effective communication
Encourage open communication between maintenance teams and other departments to facilitate the quick exchange of information and swift resolution of issues. In our experience, utilizing maintenance software across departments significantly enhances collaboration and streamlines processes, leading to improved operational efficiency.
Common pitfalls to avoid
Minimizing errors is essential for ensuring a smooth maintenance process. To achieve this, it’s crucial to avoid the following mistakes:
Insufficient planning: Lacking a clear maintenance plan can lead to unexpected breakdowns and increased costs. Prioritize thorough planning of your maintenance activities to mitigate these risks.
Ignoring data: Data is a valuable resource that should not be overlooked. Regularly analyze maintenance and operating costs to inform decision-making and continuously enhance your processes.
Neglecting training: Failing to provide regular training can leave your team ill-equipped to handle new technologies and procedures, negatively impacting efficiency. Ensure ongoing education to keep your staff up to date.
Relying on manual processes: Manual documentation is often prone to errors and can be time-consuming. Implement digital solutions to enhance transparency and streamline operations.
By systematically planning and executing maintenance activities, you can secure the long-term success of your business. Adopting effective strategies and technologies will significantly boost the efficiency of your maintenance processes, as well as enhance safety and profitability.
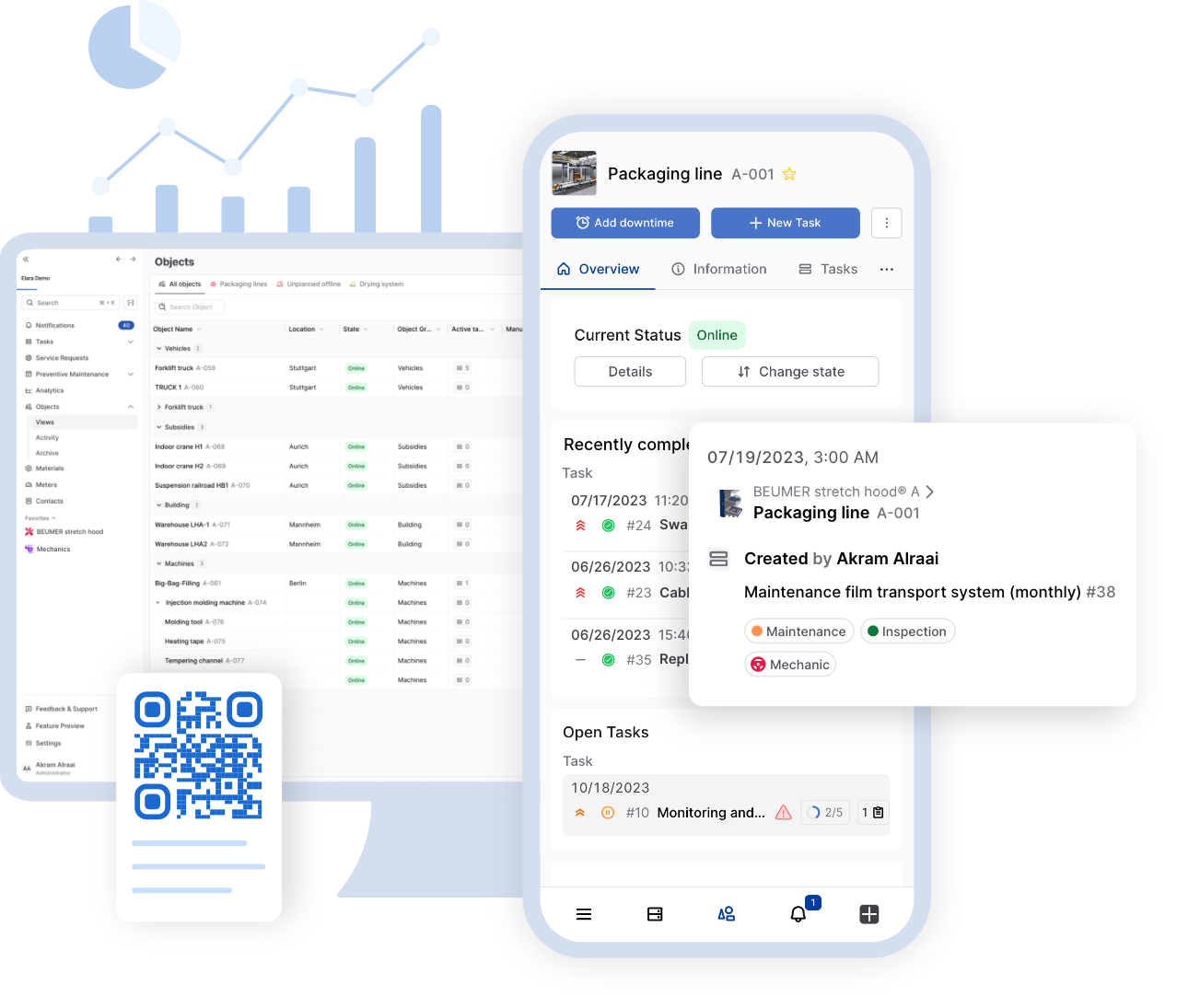
Elara’s maintenance software
Elara is here to assist you in executing all maintenance activities seamlessly:
Digital work orders: Are delays in work orders or confusing documentation hindering your operations? Elara simplifies the creation of digital work orders, enhancing transparency and fostering collaboration across workflows and departmental boundaries.
Efficient fault message processing: Unplanned interruptions can be costly. With Elara, you maintain a comprehensive overview, allowing you to minimize unexpected risks effectively.
Spare parts and material management: Downtime due to missing spare parts can be a thing of the past with Elara. Our centralized data system and real-time inventory monitoring keep you informed, ensuring you’re always prepared.
Evaluations and reports: In today’s data-driven world, insights are invaluable. Elara transforms raw data into actionable insights, enabling you to optimize your maintenance strategies.
Do you want to learn how Elara can benefit your organization? Schedule a free demo today!
[In the age of AI, you never know if you’re reading something copy and pasted directly from ChatGPT, or if an actual human sat down to write this with some cool facts from their boss or operations team. That’s why we created a short and simple introduction to how we create content at Elara.]