The enhancement of maintenance processes' efficiency and effectiveness can be achieved through the adoption of maintenance software, commonly referred to as a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS). However, [...]

The enhancement of maintenance processes’ efficiency and effectiveness can be achieved through the adoption of maintenance software, commonly referred to as a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS). However, before optimization can occur, it’s essential to master fundamental tasks such as scheduling.
This article delves into the ways maintenance software can elevate maintenance processes and outlines the initial steps required for implementation.
What are maintenance processes?
Maintenance processes encompass all methods, measures, and actions directed towards preserving, restoring, or enhancing the functionality and performance of technical systems, machinery, plants, buildings, and infrastructures.
These activities encompass servicing, inspection, repair, and enhancement. The primary objective of maintenance is to optimize machine availability and reliability, ensure safety, and prolong equipment service life, all while optimizing operating costs. Maintenance processes constitute an integral component of operational management across various industries and sectors.
Consider a consumer goods company as an illustration. Within a manufacturing plant producing mass-market goods, maintenance processes assume pivotal significance. A breakdown in the production line could severely disrupt the supply chain, impacting product availability for consumers. Thoughtfully planned and executed maintenance procedures mitigate such disruptions, ensuring seamless operations within production facilities.
Effective maintenance not only enhances the quality and reliability of manufactured products but also bolsters customer confidence and the company’s competitive edge within the industry.

Why are effective maintenance processes important?
Maintenance processes are crucial for optimizing operational efficiency. Firstly, they help in preventing unexpected breakdowns of plant and machinery, thus avoiding downtime. Secondly, efficient maintenance processes can enhance equipment performance. Well-maintained equipment operates more efficiently and yields higher output.
Regular maintenance plays a vital role in minimizing wear and tear, extending equipment life, and optimizing production capacity. Efficiently organized maintenance processes can also lead to long-term cost savings. Timely identification and resolution of issues can prevent expensive repairs or equipment replacements. Moreover, well-maintained systems contribute to workplace safety by reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Regular inspections and safety-compliant maintenance enable the timely identification and rectification of potential hazards, thereby enhancing the safety of maintenance staff.
The role of maintenance software
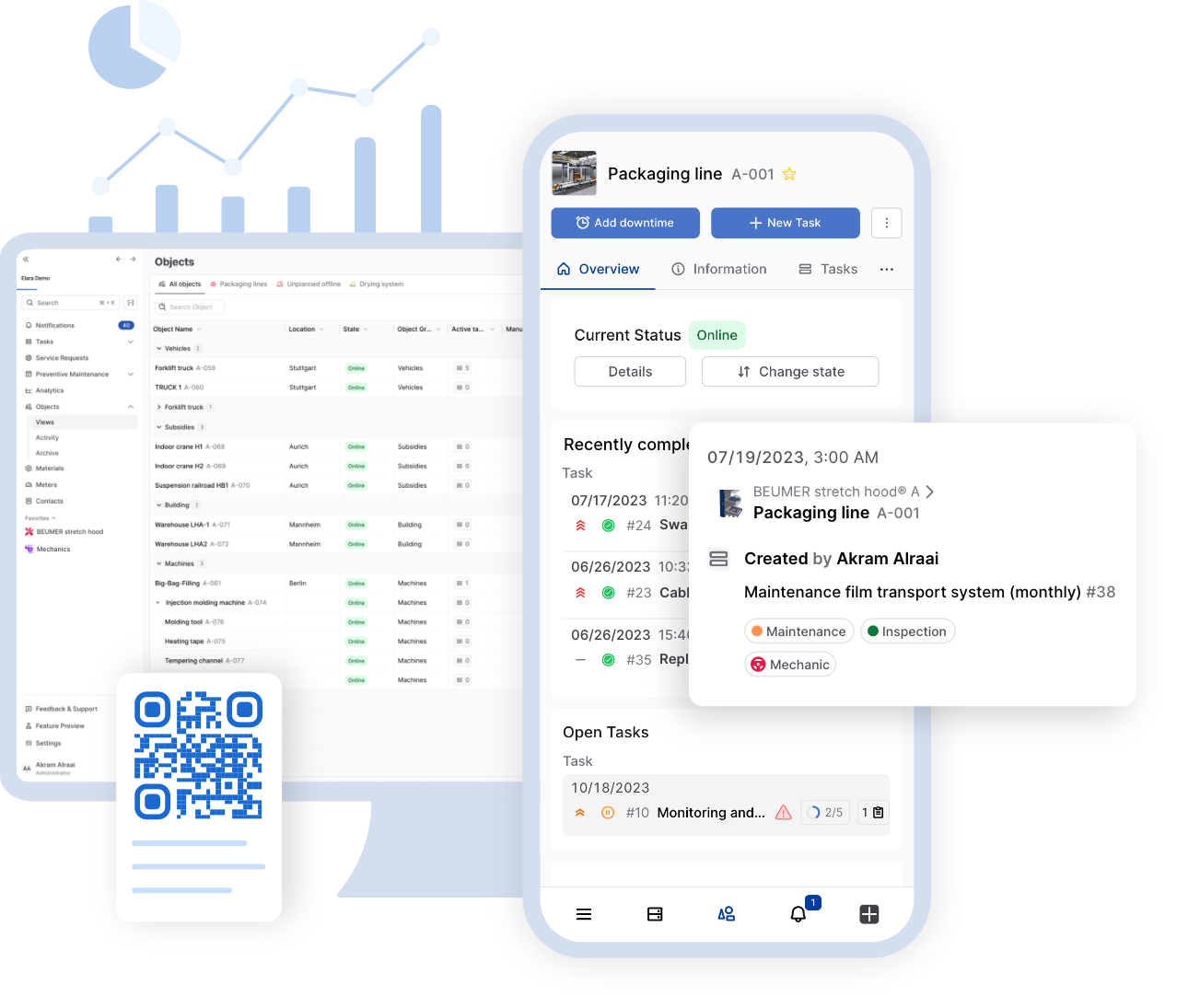
Effective maintenance processes are crucial for sustaining asset performance and preventing downtime. A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can enhance these processes by offering a variety of functions, from creating maintenance schedules to tracking operating hours.
A pivotal feature of a CMMS is the systematic planning, which simplifies the creation and management of maintenance schedules. This tool enables the maintenance team to plan and coordinate maintenance tasks using an intuitive calendar interface. The CMMS stores essential information like due dates, maintenance types, and necessary resources. Its reminder function ensures that upcoming maintenance tasks are duly noted and executed on schedule.
Moreover, a CMMS facilitates data collection and analysis, aiding in the optimization of maintenance plans and the identification of operational bottlenecks. By scrutinizing data such as operating hours and maintenance expenses, areas for improvement can be pinpointed, leading to faster and more efficient maintenance procedures.
In summary, a CMMS streamlines maintenance processes by equipping the maintenance team with the requisite tools and data for planning, monitoring, and executing maintenance tasks. The reminder feature serves as a valuable aid in ensuring the timely completion of upcoming maintenance activities.
From simple work orders to optimized maintenance processes
Clear and straightforward work orders are essential for smooth maintenance processes as they ensure that maintenance tasks are carried out correctly. This is where a CMMS can step in to enhance the work order process. Whether maintenance workers choose work orders from a list or managers assign them typically depends on the user’s preference.
Once a work order is created and assigned, it becomes accessible to the maintenance staff. A well-structured work order is crucial for ensuring that maintenance or repair work is executed effectively and efficiently.
A good work order should include:
- A description of the problem or maintenance task
- The equipment or device requiring service, previously entered into the CMMS
- A list of necessary materials, tools, and resources
- A due date or deadline for completing the maintenance
- A list of employees involved in the maintenance
- Instructions for performing the maintenance, including any special requirements or safety precautions in an interactive checklist.
While a simple title may suffice, adding extra details enhances its value for the future. Old, basic work orders can serve as templates for future maintenance tasks, gradually accumulating more details over time to form a valuable knowledge base for the maintenance team.
Storing work orders as templates in a CMMS can also expedite and improve the efficiency of the maintenance team, particularly during the training of new employees. New team members can refer to these templates to quickly grasp how maintenance tasks are conducted and what steps are involved. For recurring issues, modern CMMS solutions facilitate swift history searches, aiding in promptly identifying solutions.
Integrate meters into maintenance software
Once companies have established basic work orders and maintenance schedules based on time intervals, they can advance their maintenance planning by incorporating hour meters into their maintenance software.
An example of this is using hour meters for machines that require maintenance after specific hour milestones, like initial maintenance after 1,000 hours and then every 500 hours thereafter.
In a CMMS, machine hours can be monitored, and maintenance tasks can be automatically triggered once certain hour thresholds are reached. This enables the maintenance team to schedule and carry out preventive maintenance before any breakdown occurs.
Additionally, other parameters and meters, such as sensors for temperature or pressure, can be integrated into maintenance software. However, it’s essential to recognize that introducing numerous features at once can overwhelm companies new to maintenance software implementation. Therefore, it’s advisable to maintain a clear focus and incorporate additional functionality gradually as the team becomes accustomed to it.

Practical example of maintenance software implementation
When our customer—a medium-sized company in the logistics sector—implemented Elara’s maintenance software, it was crucial to accurately record all the necessary work. The maintenance team began by documenting all activities and creating simple work orders to track upcoming maintenance tasks.
Over time, they progressed to scheduling work orders for future maintenance using the CMMS calendar function, improving organization and coordination. This made their day-to-day tasks easier and boosted maintenance process efficiency.
With continued use of the maintenance software, our customer gained deeper insights into their equipment. They soon recognized the value of maintaining certain equipment parts at fixed intervals to prevent breakdowns. Gradually, they introduced preventive maintenance by integrating it into the software’s scheduler. This ensured employees were consistently reminded of maintenance intervals, and documentation became almost automatic.
Looking ahead, our customer plans to enhance maintenance planning by integrating hour meters into the maintenance software for more precise maintenance and repair scheduling.
Elara’s point of view
Implementing maintenance software offers numerous benefits to organizations, including enhancing maintenance processes, minimizing downtime, and boosting asset performance. At Elara, we believe that implementing this software can be simplified by concentrating on specific areas, such as simple work orders or maintenance by time intervals, and gradually implementing them.
At Elara, we’re dedicated to assisting our customers in implementing these innovative solutions and enhancing their operational efficiency further.
Discover how B-Plast enhanced their maintenance processes with Elara.
[In the age of AI, you never know if you’re reading something copy and pasted directly from ChatGPT, or if an actual human sat down to write this with some cool facts from their boss or operations team. That’s why we created a short and simple introduction to how we create content at Elara.]