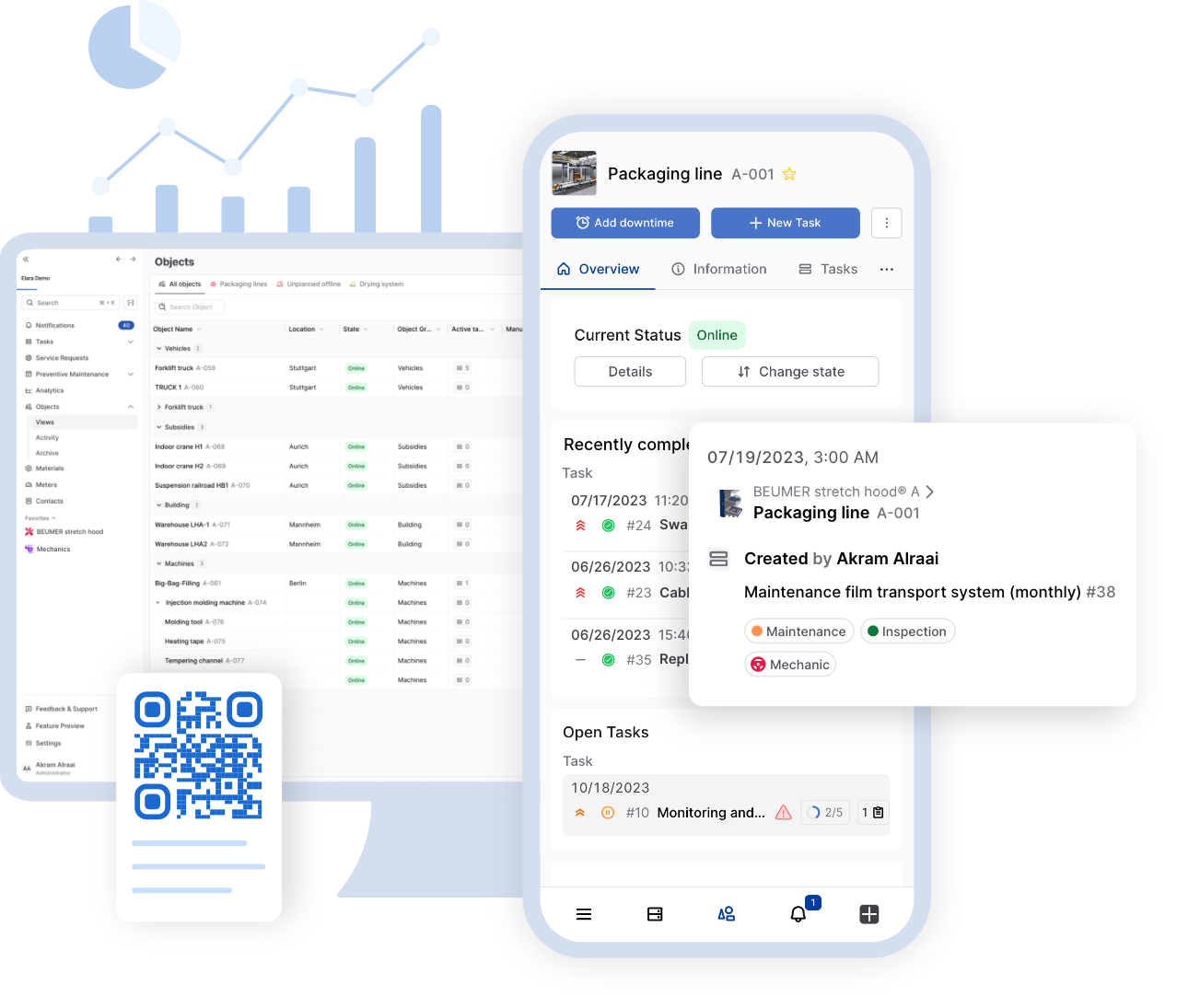
In modern industrial production, obsolescence management has become a critical factor in ensuring efficient operations and minimizing costs. The term "obsolescence" refers to the challenge that exists when [...]
In modern industrial production, obsolescence management has become a critical factor in ensuring efficient operations and minimizing costs. The term “obsolescence” refers to the challenge that exists when parts or components in a plant or production line are no longer available, whether due to technological advancement, economic factors or the manufacturer discontinuing production. This can lead to unexpected production stoppages, which are not only costly but can also have a disruptive impact on supply chains.
In this article, we explore how companies can address these challenges through proactive obsolescence management. We will look at strategies and best practices that enable companies to ensure the availability of critical parts, minimize supply bottlenecks and increase the flexibility of their production processes. By implementing effective obsolescence management strategies, companies can not only improve their operational efficiency, but also strengthen their competitiveness in a dynamic market environment. Join us on this journey through the world of obsolescence management and learn how you can optimally prepare your company for future challenges.
What is obsolescence management?
Obsolescence management refers to the systematic management of the challenges that can arise from the obsolescence and unavailability of parts or components.
This obsolescence can have various causes:
- Technical obsolescence: New technologies and advancements make existing products or components obsolete or unusable. This can be due to the introduction of new standards, improved materials or technical innovations.
- Economic obsolescence: Manufacturers may decide to discontinue the production of certain products for economic reasons. This can lead to spare parts and components no longer being available, even if the technical functionality is still present.
- Functional obsolescence: Changes in requirements or standards may mean that certain parts or components no longer meet current functions or safety standards. This may relate to regulatory requirements or market preferences.
Obsolescence management aims to identify these risks at an early stage and take appropriate measures to minimize the impact on production. This includes, among other things:
- The identification of discontinued parts and their potential impact on production.
- The development of alternative sourcing strategies, including the search for spare parts from other suppliers or the search for alternative products with similar functions.
- Implementing a robust information management system that continuously monitors and updates the availability and status of parts.
Effective obsolescence management enables companies to react flexibly to changes in the supply chain and ensure the continuity of their production processes. Obsolescence expert Dr. Wolfgang Heinbach underlines this, as he sees obsolescence as unavoidable and for this very reason he believes it is worthwhile for companies to tackle it head on. In the next section, we will look at strategies on how companies can proactively deal with obsolescence to maximize their operational efficiency and strengthen their competitiveness.

Challenges of obsolescence and their impact
Obsolescence presents several challenges for companies that can directly affect their production processes and overall efficiency. These challenges include:
- Costs and risks from unplanned production downtime: Unplanned failures due to the unavailability of discontinued parts can incur significant costs. Production lines may come to a halt, leading to delays in product delivery and potentially straining customer relationships. Repairing or replacing machinery often becomes exponentially more expensive when rapid solutions are needed.
- Dependence on discontinued parts and global supply chains: Many companies rely heavily on global supply chains to meet their production needs. When discontinued parts cannot be sourced in time, it can lead to substantial delays. Finding alternative suppliers or replacement parts can be time-consuming and costly. Additionally, geopolitical events or trade restrictions can further impact availability.
- Impact on product quality and safety: Using unspecified or unauthorized replacement parts can compromise the quality and safety of end products. This may result in increased rejection rates or even pose safety risks to end-users, especially in critical industries such as aerospace or medical technology.
To address these challenges, proactive obsolescence management is crucial. In the next section, we will look at strategies for how companies can minimize these risks by focusing on transparent information flows, alternative sourcing strategies and long-term planning.
Strategies for effective obsolescence management
To tackle the challenges of obsolescence effectively, companies can implement several strategies designed to minimize downtime and reduce costs:
- Proactive procurement planning: early identification of discontinued parts
A key aspect of obsolescence management is the early identification of discontinued parts. Companies should regularly maintain supplier contacts and stay alert to announcements regarding product changes or discontinuations. By capturing this information early, companies can better prepare and plan alternative procurement routes in advance. - Utilizing alternative sources and suppliers: benefits and risks
Leveraging alternative sources and suppliers can be crucial for avoiding shortages. Building a diversified supply chain allows companies to respond flexibly to changes. However, this approach also carries risks, such as longer lead times or variations in quality. Therefore, companies should carefully evaluate alternative sources and implement risk management strategies as needed. - Implementing a structured obsolescence management system
A structured obsolescence management system is essential for ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of obsolescence measures. This system should include clearly defined processes, from identifying discontinued parts to implementing procurement strategies. Integrating this system into existing procurement and production processes helps companies act promptly and minimize shortages.

Best Practices
- Regular review and updates: Continuously review and update obsolescence databases and strategies to identify new risks early on.
- Collaboration with suppliers: Foster close collaboration with suppliers and partners to quickly obtain information on product changes or discontinuations and develop joint solutions.
- Training and awareness: Provide training for employees on obsolescence management and raise awareness about the impact of discontinued parts on production and quality.
- Tracking installed parts and prioritizing by obsolescence risk: Effective obsolescence management requires not only integrating new components but also systematically tracking installed parts and their quantities. This allows for targeted assessment and prioritization of obsolescence risks, with critical components that could significantly disrupt production processes being given top priority.
- Software updates for controls, monitoring, and analytics: Regular updates to control systems, monitoring software, and analytics tools are crucial for maintaining system compatibility, safety, and minimizing potential vulnerabilities. Proactive planning and prioritization ensure that equipment is well-prepared for future challenges and maintains long-term availability.
By implementing these strategies and best practices, companies can enhance their resilience to obsolescence risks and improve the efficiency of their production processes.
Benefits of effective obsolescence management
Effective obsolescence management offers numerous advantages that directly impact production processes and overall competitiveness.
- Reduction of downtime and costs
By identifying and managing discontinued parts proactively, companies can achieve significant cost savings. Downtime due to missing parts is minimized, as alternative procurement routes are prepared in advance. This results in reduced downtime, fewer emergency measures, and overall lower maintenance and production costs. - Increased flexibility and resilience in the supply chain
A well-designed obsolescence strategy enhances supply chain flexibility. Companies can quickly adapt to changes in part availability by utilizing alternative sources or transitioning to successor products in a timely manner. This reduces the risk of supply shortages and ensures more stable production, even in the face of unforeseen changes or challenges in the supply chain. - Optimization of inventory and resource utilization
Precise planning and forecasting for discontinued parts allow companies to optimize their inventory. By avoiding excessive stock or shortages, resources are used more efficiently. This, in turn, lowers inventory holding costs and reduces capital tied up in unnecessary stock.
A robust obsolescence management system is not just a preventive measure against unexpected production disruptions but also a strategic approach to enhancing operational efficiency and flexibility. Companies that invest in effective obsolescence management can strengthen their competitiveness and secure their market position in the long term.
Elara’s vision for the future
The future of obsolescence management will increasingly be shaped by technological advancements and data-driven solutions. Cloud-based platforms and IoT integrations will play a crucial role in enhancing transparency and control over the supply chain.
It is also essential for new parts or components to be seamlessly integrated into existing systems and processes upon their introduction. This requires careful analysis to ensure that successor products are not only technically compatible but also meet functional requirements and safety standards. In particular, in the realm of Operational Technology (OT), where operational technology and production systems are closely interconnected, the selection of inappropriate parts can have severe impacts on efficiency and safety. By conducting thorough evaluations and involving all relevant stakeholders, companies can ensure that the introduction of successor products proceeds smoothly and that operational continuity is maintained.
With a clear focus on the future of obsolescence management, companies are well-positioned to not only address current challenges but also to achieve long-term success and differentiate themselves in the market.
Want to see what our customers are saying about Elara? Check out our success stories.
[In the age of AI, you never know if you’re reading something copy and pasted directly from ChatGPT, or if an actual human sat down to write this with some cool facts from their boss or operations team. That’s why we created a short and simple introduction to how we create content at Elara.]